Using the Terminal in RcloneView
RcloneView includes a built-in Terminal so you can run full rclone CLI commands without opening CMD, PowerShell, or a system shell. It is ideal for quick tests, managing remotes, or capturing logs while staying inside the app.
This guide covers how to open the Terminal, run rclone commands, expand/shrink the view, and use copy options to share results.
Open the Terminal
- Click the
Terminaltab at the bottom of RcloneView.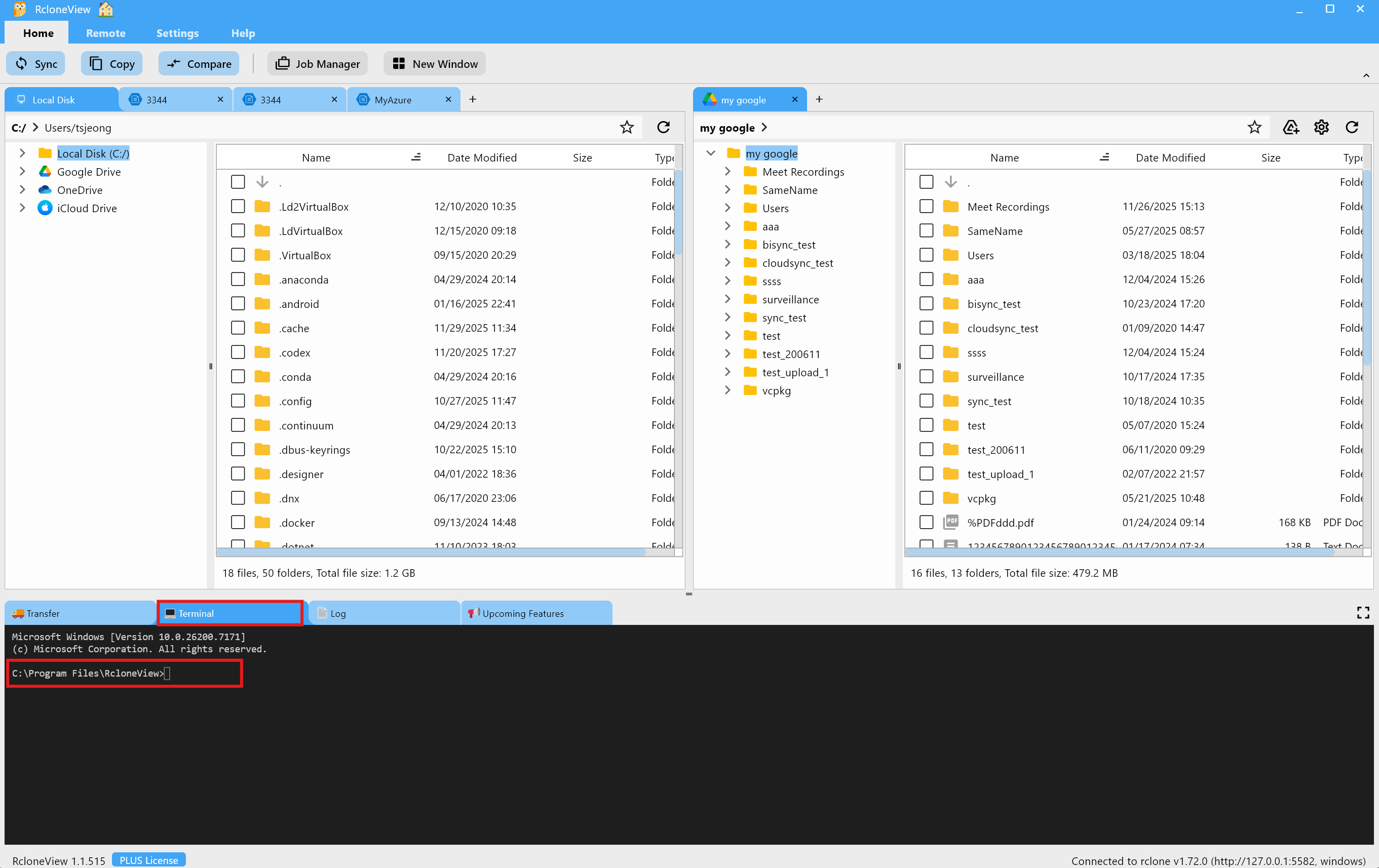
- The Terminal works like the standard
rclonecommand-line interface and runs commands in the current RcloneView context.
List Available rclone Commands
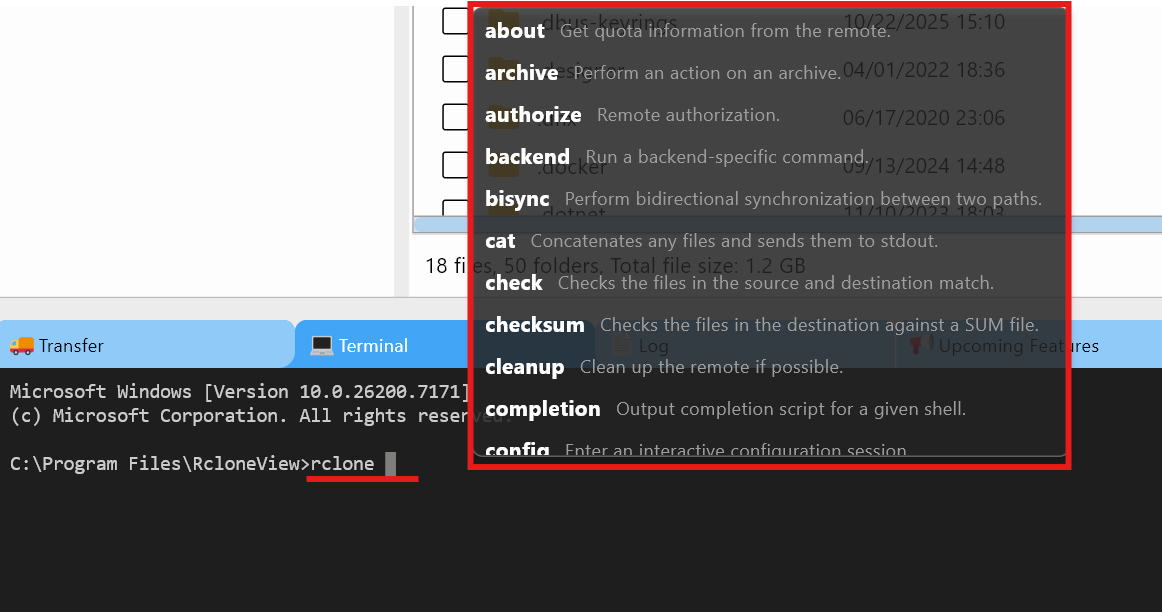
Type rclone and press the space bar to automatically display all supported commands.
View Help and Remote Details (rclone about)
- For general help on
about: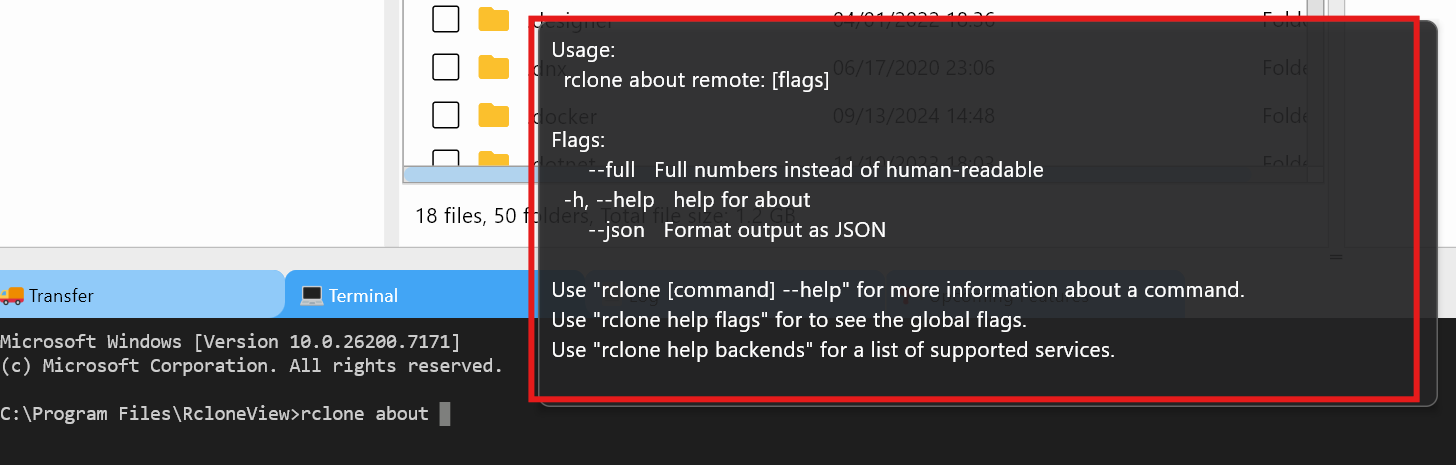
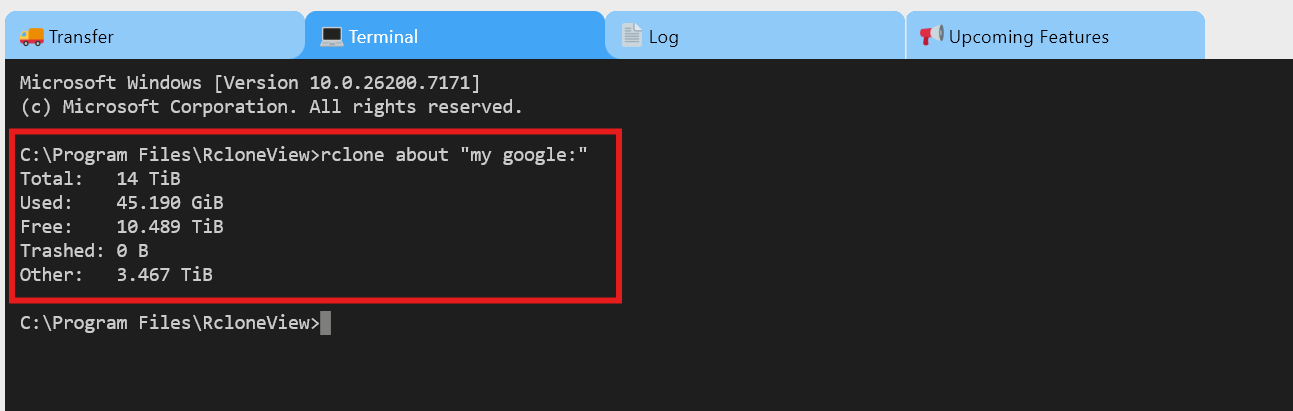
- To get storage info for a specific remote (example:
mygoogle):rclone about "mygoogle:"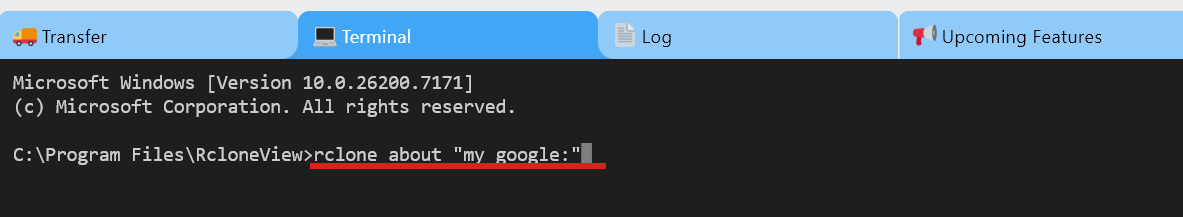
Result example:
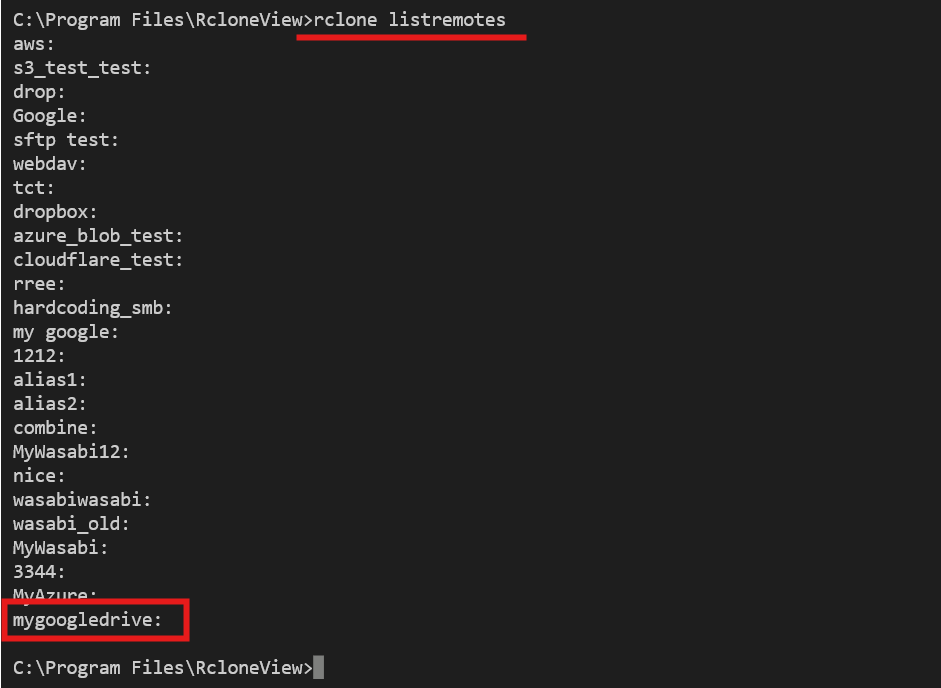
List All Configured Remotes
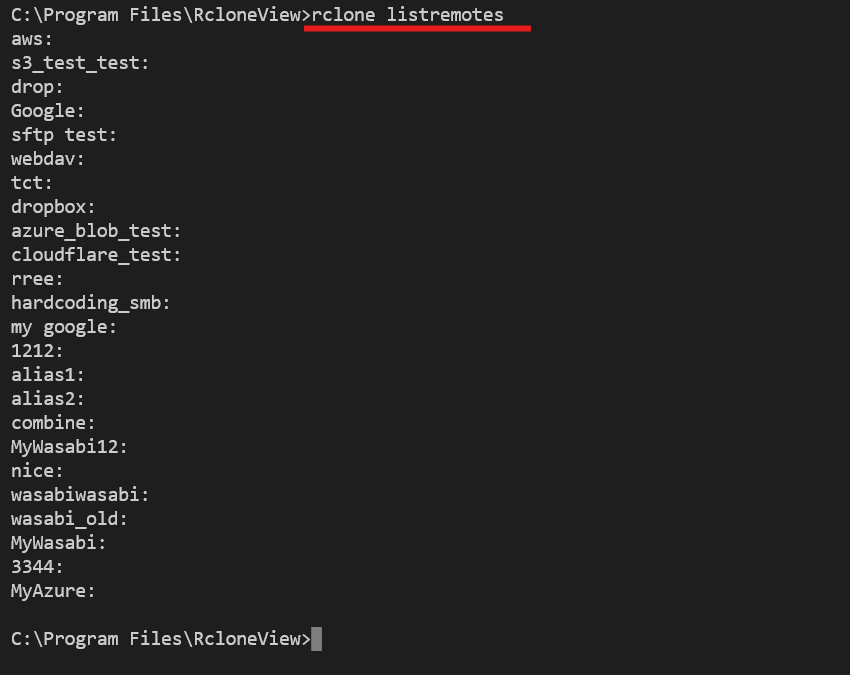
Use the listremotes command to confirm which remotes are available:
rclone listremotes
Expand or Shrink the Terminal View
- Expand: Switch to full-screen Terminal for long outputs.
- Shrink: Return to the default layout.
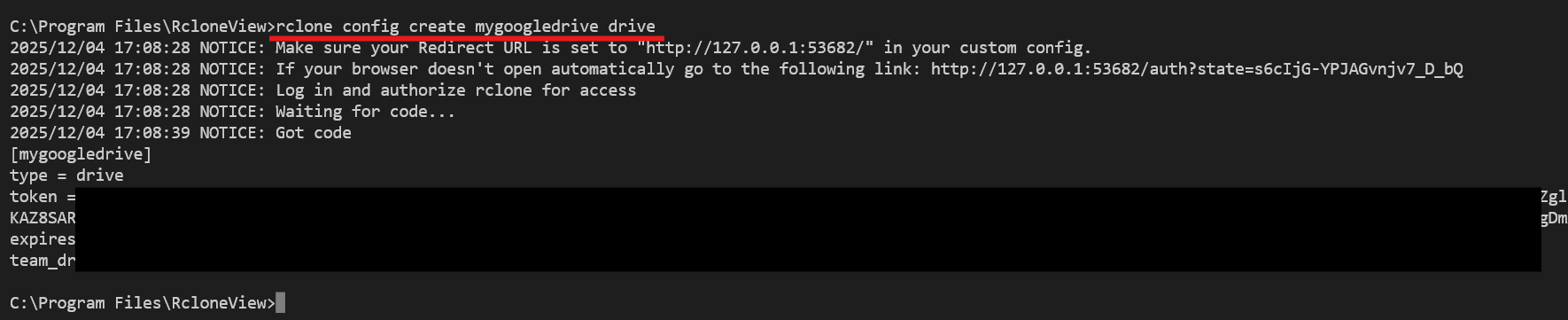
Create a Remote via CLI (rclone config create)
Example: create a Google Drive remote named mygoogledrive and verify it:
rclone config create mygoogledrive drive
rclone listremotes
Copy, Paste, and Copy All
Select any Terminal output to open the context menu and choose Copy, Paste, or Copy All.
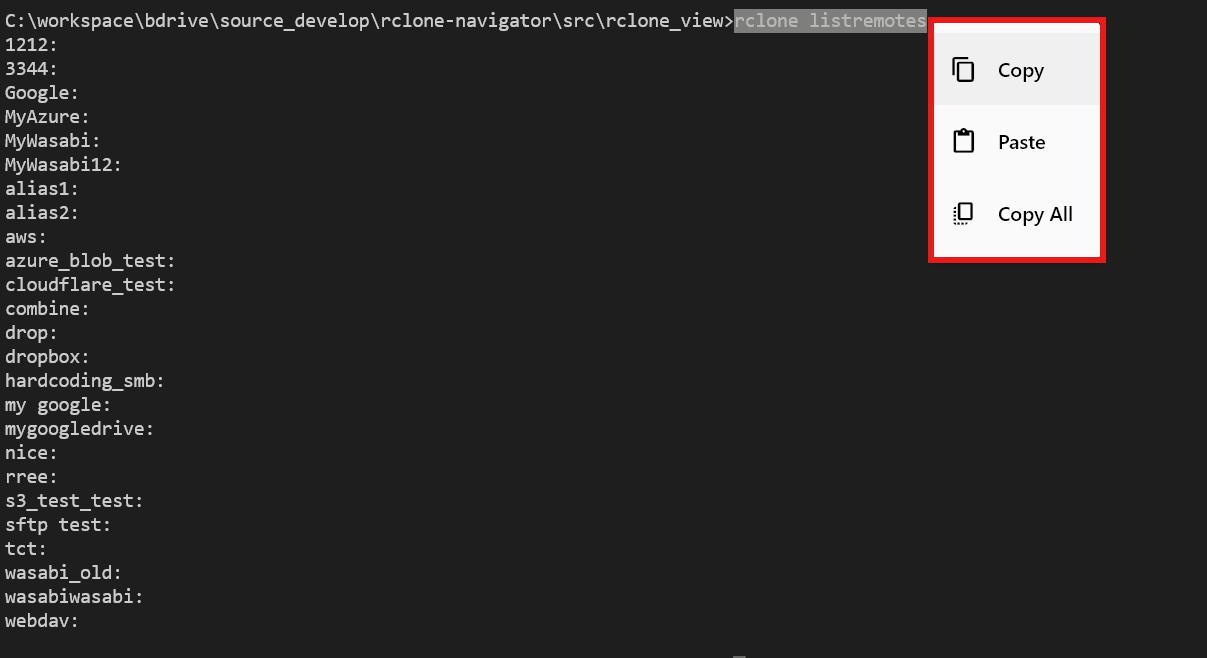
This is helpful for sharing logs with support or saving results to documentation.
Recommended Use Cases
- Test advanced
rclonecommands (lsf,tree, backend flags) before automating. - Validate scripts or server-side commands inside RcloneView.
- Quickly manage or create remotes when the GUI path is slower.
Commands such as delete, purge, or incorrect sync flags can remove data permanently. Double-check paths and remotes before running them in the Terminal.