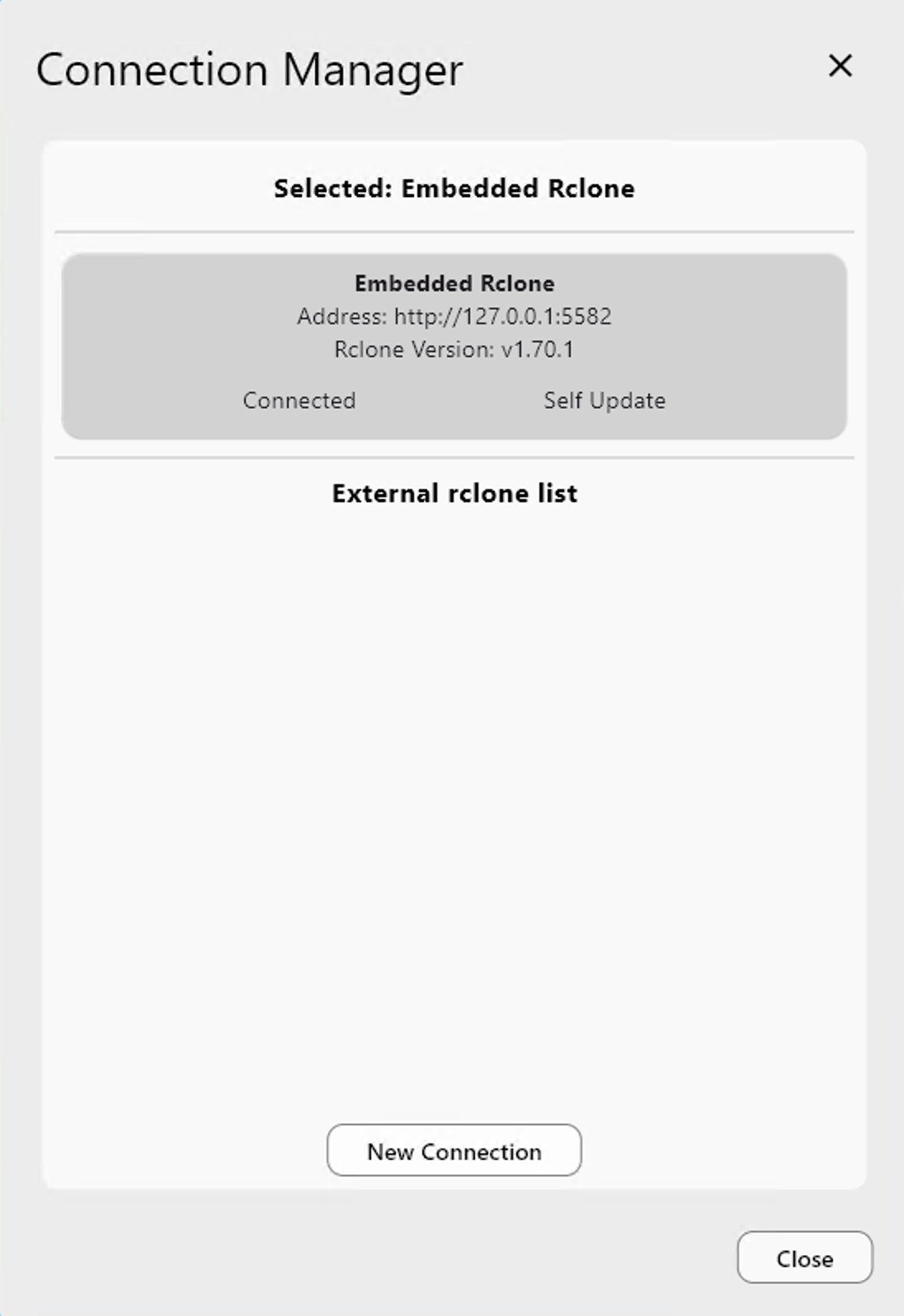
RcloneView Connection Manager: Switch Embedded vs External rclone for Safer Cloud Operations
Need a clean separation between personal jobs, production data, and test environments? RcloneView Connection Manager lets you switch rclone instances in seconds -- no CLI risk.
RcloneView includes an Embedded rclone engine, but it also connects to External rclone instances (local, remote, or container). This gives you a safe way to isolate environments, test changes, and operate at enterprise scale without rewriting configs or juggling terminals.
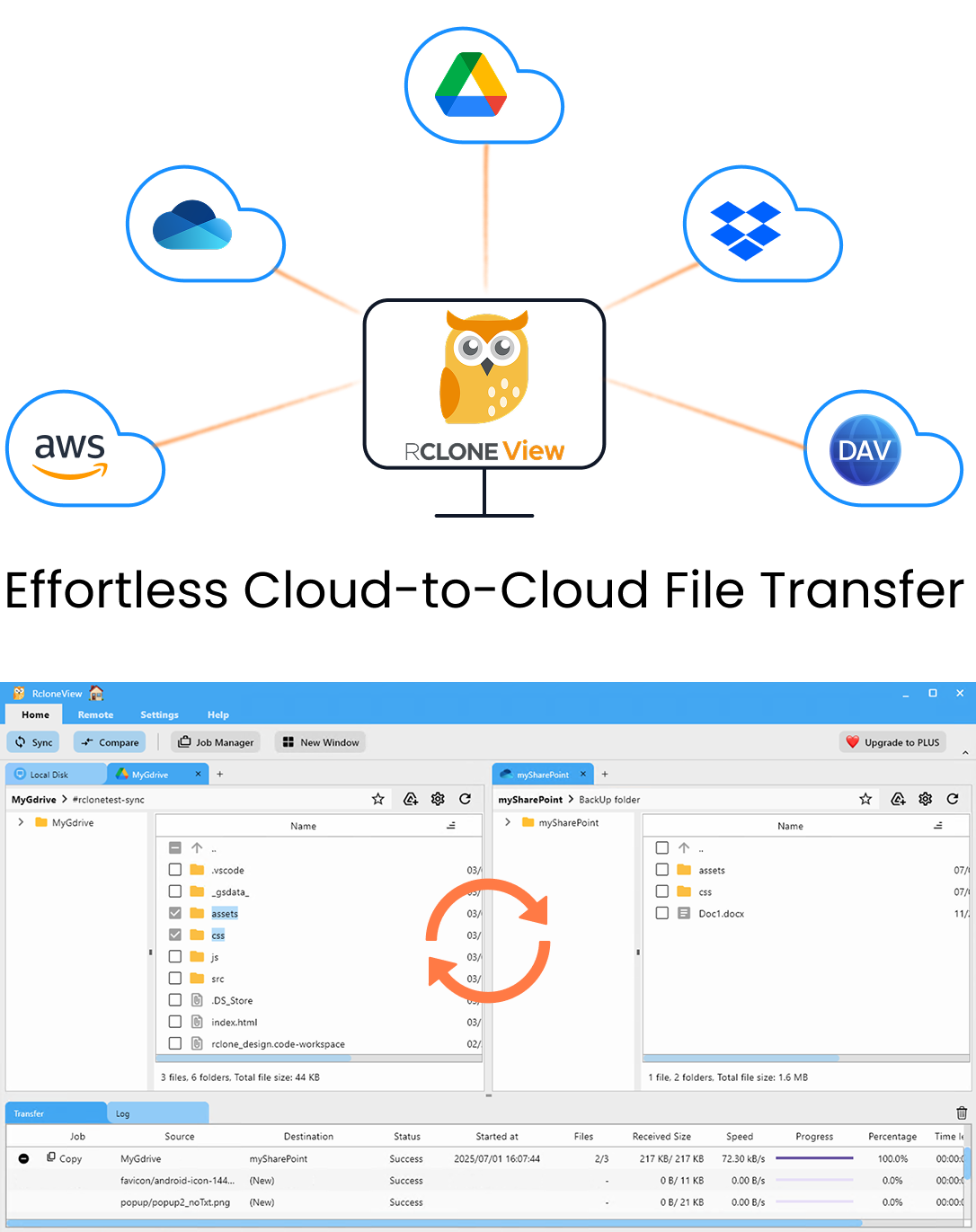
Manage & Sync All Clouds in One Place
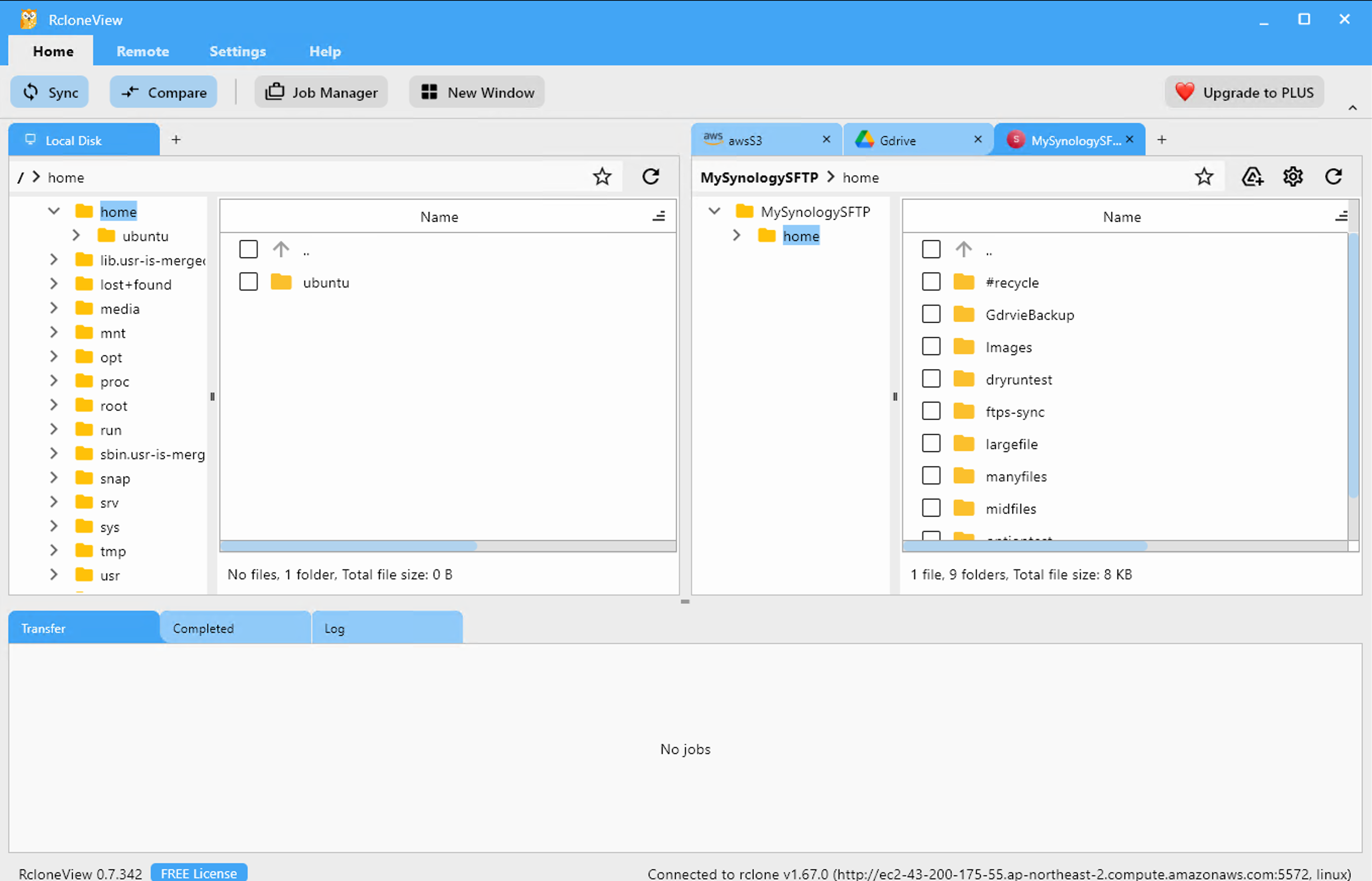
RcloneView is a cross-platform GUI for rclone. Compare folders, transfer or sync files, and automate multi-cloud workflows with a clean, visual interface.
- One-click jobs: Copy · Sync · Compare
- Schedulers & history for reliable automation
- Works with Google Drive, OneDrive, Dropbox, S3, WebDAV, SFTP and more
Free core features. Plus automations available.
Why Connection Manager matters
Most rclone users eventually face one of these problems:
- A test run alters production remotes
- One machine needs different credentials than another
- You want a remote server to do transfers while your PC stays clean
Connection Manager solves this by letting you switch between Embedded and External rclone instances with a single click.
Embedded vs External rclone (quick mental model)
- Embedded rclone: bundled, local, and always available
- External rclone: user-managed, can run on a server, NAS, or separate machine
This is the foundation for safe workflows: isolate environments instead of mixing them.
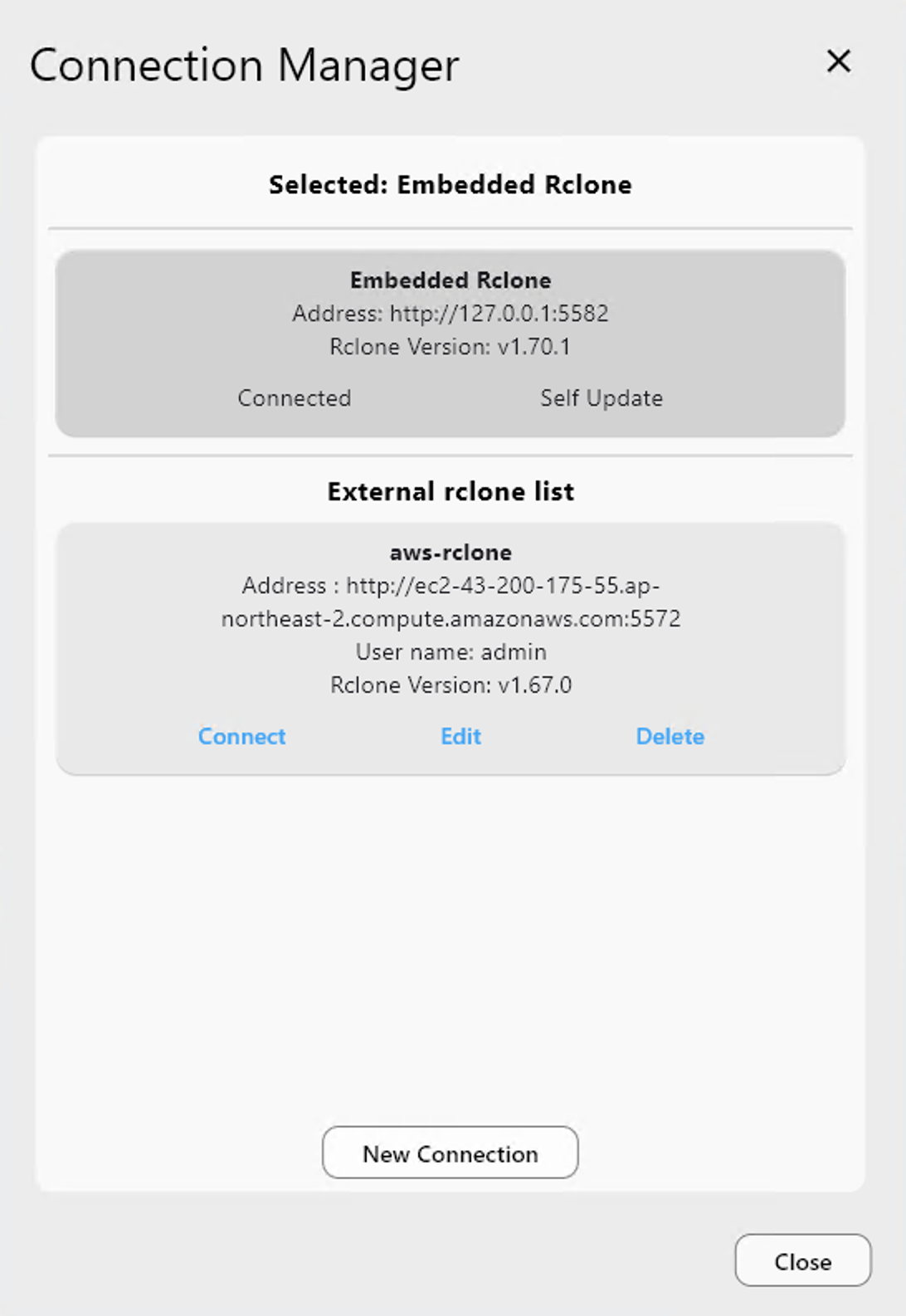
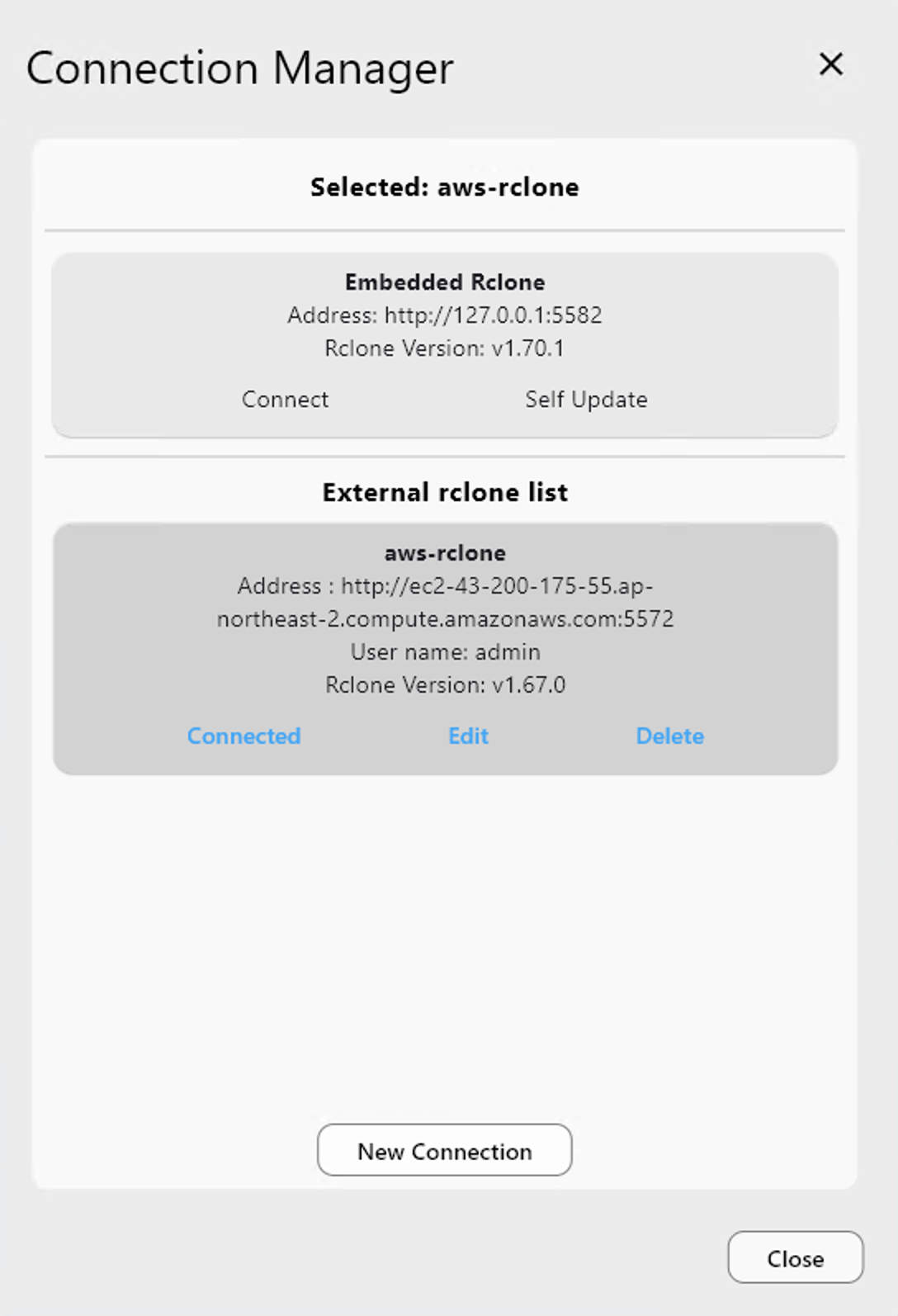
What the Connection Manager does
Connection Manager lets you:
- See all available rclone instances
- Connect to one at a time
- Switch between Embedded and External instantly
- Keep configurations isolated per instance
Why this is a high-value workflow for teams
1) Safer testing and validation
Use an external instance to test changes without touching production remotes.
2) Clean separation of environments
Run one instance for staging, another for production. No mixed configs.
3) Remote compute for heavy transfers
Let a server or NAS handle large transfers while your desktop stays lightweight.
4) Faster recovery from mistakes
If an external instance fails or misbehaves, switch back to Embedded instantly.
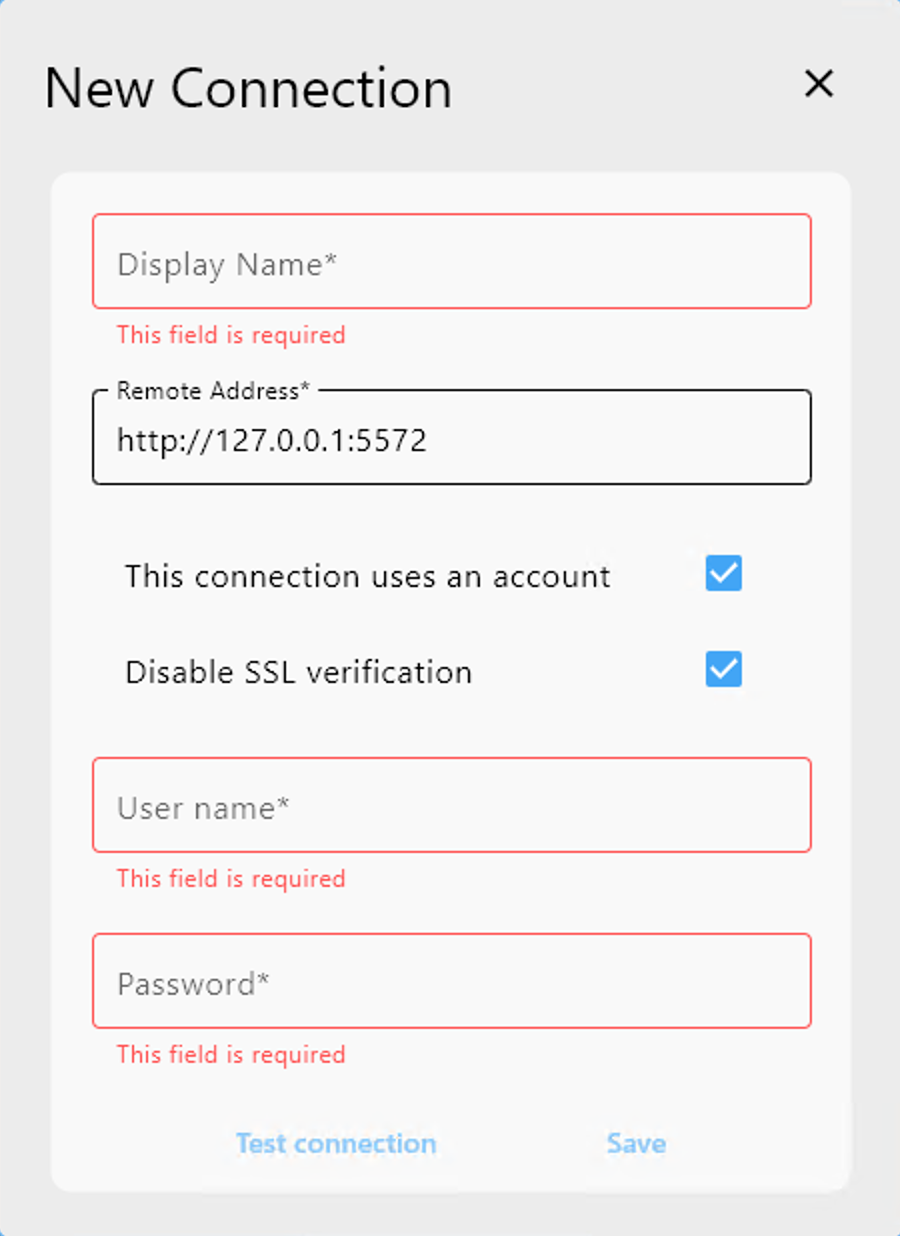
Step-by-step: add an External rclone connection
- Open Settings -> Connection Manager.
- Click New Connection.
- Enter the remote address for
rclone rcd.
Once added, you can connect, edit, or delete the entry.
Guide: /support/howto/rcloneview-basic/connection-manager
Typical use cases
Personal vs business isolation
Keep personal remotes in Embedded, business remotes in External.
Server-side transfers
Run rclone on a server (EC2, NAS, or Docker). Use RcloneView as the UI controller.
Multi-window operations
Open a new RcloneView window to manage another instance without switching.
Best practices for reliable workflows
- Name external instances clearly (e.g.,
Prod-Rclone,Lab-Rclone). - Keep job schedules tied to the correct instance.
- Use Compare before Sync when switching environments.
- Document which remotes live in each instance.
Common mistakes to avoid
- Running production jobs on a test instance
- Sharing one external instance for unrelated teams
- Forgetting which instance is currently active
Connection Manager fixes most of these with visual context and quick switching.
Conclusion
RcloneView Connection Manager turns rclone into a safe, multi-environment system. Embedded is perfect for everyday use. External is ideal for isolation, server-side transfers, and enterprise workflows. Switch as needed and keep operations clean.